NfL in Blood Foretells Poor Brain Health After the Heart Stops
Quick Links
Neurofilament light protein might be useful in cardiovascular emergency medicine, not just in neurology. A blood test could allow doctors to predict brain damage after a cardiac arrest, according to an October 29 paper in JAMA Neurology. Scientists led by Tobias Cronberg, Lund University, and Kaj Blennow, University of Gothenburg, Mölndal, both in Sweden, report that the concentration of neurofilament light chain protein, measured in blood up to three days after the arrest episode, strongly indicates a person's neurologic outcome six months later. Plasma NfL foretold long-term consequences better than any other method used to assess brain function.
- Cardiac arrest damages the brain.
- Plasma NFL indicates how severe the damage is.
- Could this blood test foretell whether a patient will emerge from coma?
“It’s extremely interesting to see a marker reflect the extent of neuronal injury as well as NfL does,” said Marion Moseby-Knappe, co-first author on the paper with Niklas Mattsson, both from Lund University.
Axonal NfL forms part of the neuronal cytoskeleton, and its appearance in the cerebrospinal fluid or blood is a sure sign of neuronal injury. NfL is being examined as a biomarker in neurologic conditions ranging from Alzheimer’s to repetitive mild traumatic brain injury and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (AlzBiomarker; Sep 2016 news; Mar 2017 news).
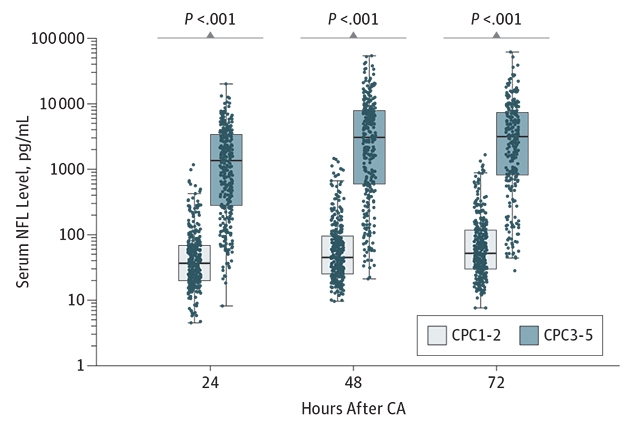
Ominous Marker. Patients with high NfL in their blood at 24, 48, and 72 hours after a cardiac arrest have low neurologic function scores six months later. Note Y-axis uses logarithmic scale. [©2018 American Medical Association. All rights reserved.]
Two small studies had previously correlated elevated blood NFL with poor neurologic outcomes after cardiac arrest (Rana et al., 2013; Rundgren et al., 2012). To expand the finding, Moseby-Knappe and colleagues used a Simoa-based assay to measure serum NfL up to 72 hours after cardiac arrest in 717 patients, all of whom were unconscious and hospitalized. Six months later, she measured neurologic outcomes using the Cerebral Performance Category scale. The CPC rates the health of a person’s brain from 1 to 5. At the six-month mark, 313 people in this study tested normally (1 on the CPC), 44 had a mild impairment such as seizures or memory loss (2 on the CPC), 28 had a severe disability such as paralysis or dementia (3), eight remained comatose (4), and 324 had suffered brain death (5).

NfL Can Tell.
Serum neurofilament light predicts six-month brain outcome with higher specificity and sensitivity than tau, NSE, or S100. [©2018 American Medical Association. All rights reserved.]
Patients scoring a 1 or 2 had nearly 40 times lower serum NfL levels soon after their heart stopped than patients scoring 3 to 5 (see image above). The difference was an average of 37 pg/mL versus a whopping 1,426 pg/mL at 24 hours. Each higher CPC score had a higher NfL than the last; levels were highest for people whose CPC was 4 or 5.
Serum NfL predicted long-term outcome better than CT scans, electroencephalography, or clinical examination; it also beat the biomarkers S100 and neuron-specific enolase (see image at right). Its specificity was 98 percent, sensitivity 69 percent.
The results suggest that serum NfL could help doctors predict long-term outcomes after cardiac arrest, the authors wrote. This could be added to the battery of clinical assessments already used to help predict with greater confidence which patients will and won’t wake up from their coma and recover brain function, said Moseby-Knappe. This can help inform decisions about how long to maintain life support.—Gwyneth Dickey Zakaib
References
News Citations
- Axon Damage May Hinder Recovery from Concussion, Spark Neurodegeneration
- Neurofilament Light Chain as Prognostic Biomarker in ALS
Paper Citations
- Rana OR, Schröder JW, Baukloh JK, Saygili E, Mischke K, Schiefer J, Weis J, Marx N, Rassaf T, Kelm M, Shin DI, Meyer C, Saygili E. Neurofilament light chain as an early and sensitive predictor of long-term neurological outcome in patients after cardiac arrest. Int J Cardiol. 2013 Sep 30;168(2):1322-7. Epub 2012 Dec 31 PubMed.
- Rundgren M, Friberg H, Cronberg T, Romner B, Petzold A. Serial soluble neurofilament heavy chain in plasma as a marker of brain injury after cardiac arrest. Crit Care. 2012 Dec 12;16(2):R45. PubMed.
Other Citations
Further Reading
Papers
- Rosén C, Rosén H, Andreasson U, Bremell D, Bremler R, Hagberg L, Rosengren L, Blennow K, Zetterberg H. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in cardiac arrest survivors. Resuscitation. 2014 Feb;85(2):227-32. Epub 2013 Nov 11 PubMed.
Primary Papers
- Moseby-Knappe M, Mattsson N, Nielsen N, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Dankiewicz J, Dragancea I, Friberg H, Lilja G, Insel PS, Rylander C, Westhall E, Kjaergaard J, Wise MP, Hassager C, Kuiper MA, Stammet P, Wanscher MC, Wetterslev J, Erlinge D, Horn J, Pellis T, Cronberg T. Serum Neurofilament Light Chain for Prognosis of Outcome After Cardiac Arrest. JAMA Neurol. 2019 Jan 1;76(1):64-71. PubMed.
Annotate
To make an annotation you must Login or Register.

Comments
No Available Comments
Make a Comment
To make a comment you must login or register.