Mutations
MAPT K369I
Quick Links
Overview
Pathogenicity: Frontotemporal Dementia : Pathogenic
Clinical
Phenotype: Frontotemporal Dementia, Tauopathy consistent with Pick's Disease
Reference Assembly: GRCh37/hg19
Position: Chr17:44096092 A>T
dbSNP ID: rs63751264
Coding/Non-Coding: Coding
DNA
Change: Substitution
Expected RNA
Consequence: Substitution
Expected Protein
Consequence: Missense
Codon
Change: AAA to ATA
Reference
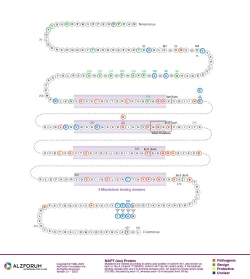
Isoform: Tau Isoform Tau-F (441 aa)
Genomic
Region: Exon 12
Findings
This mutation was identified in a 50-year-old woman of German origin presenting first with depression and dramatic personality changes, followed by loss of cognitive function. The patient continued to deteriorate and died at the age of 61. Family history was unavailable, and therefore it was not possible to assess whether the mutation segregated with disease. The mutation was not found in 100 cognitively healthy controls (Neumann et al., 2001).
Neuropathology
Postmortem examination showed brain atrophy, which was most pronounced in the temporal lobes. Numerous tau-positive Pick bodies and Pick cells indistinguishable from those of sporadic Pick's disease were observed in the neocortex, hippocampus, and subcortical brain regions (Neumann et al., 2001).
Biological Effect
Recombinant tau proteins with the K369I mutation showed reduced ability to promote microtubule assembly (Neumann et al., 2001).
Last Updated: 16 Feb 2023
References
Paper Citations
- Neumann M, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Crowther RA, Smith MJ, Spillantini MG, Goedert M, Kretzschmar HA. Pick's disease associated with the novel Tau gene mutation K369I. Ann Neurol. 2001 Oct;50(4):503-13. PubMed.
Further Reading
Learn More
Protein Diagram
Primary Papers
- Neumann M, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Crowther RA, Smith MJ, Spillantini MG, Goedert M, Kretzschmar HA. Pick's disease associated with the novel Tau gene mutation K369I. Ann Neurol. 2001 Oct;50(4):503-13. PubMed.
Alzpedia
Disclaimer: Alzforum does not provide medical advice. The Content is for informational, educational, research and reference purposes only and is not intended to substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek advice from a qualified physician or health care professional about any medical concern, and do not disregard professional medical advice because of anything you may read on Alzforum.

Comments
No Available Comments
Make a Comment
To make a comment you must login or register.